Osgood-Schlatter Disease (Knee Pain)
Types, Causes, Symptoms, Risk Factors, Complications, Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment
What are the symptoms of Osgood-Schlatter Disease?
The main symptoms indicating that a person is suffering from this disease are:
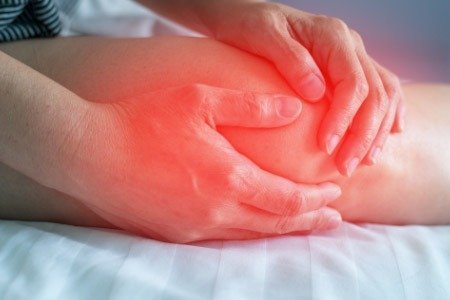
- Recurring pain in the knee or leg
- Tenderness in the knees
- Swelling right below the knee cap
- Warmth, limping, constant discomfort to the individual




 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More