Discoid Meniscus
Types, Causes, Symptoms, Complications, Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment
What is Discoid Meniscus?
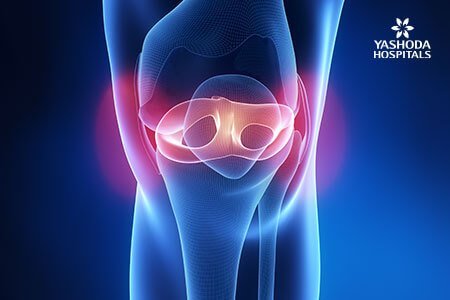
Discoid meniscus is a rare condition that affects the lateral meniscus present in the knee. It sometimes may present itself in the form of swelling, pain and cracking sound of the affected knee.




 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More