FDG PET/CT in Isolated Mediastinal IgG4 Related Disease

Background
A 33 year old man on routine annual health check-up was found to have an opacity in the right suprahilar region on chest X-ray.
Diagnosis
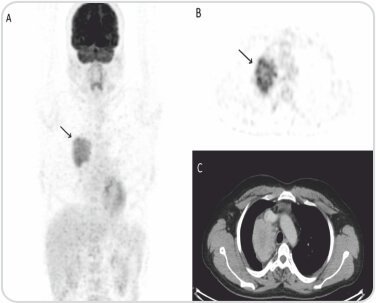
CECT thorax done for further evaluation revealed soft tissue mass in the mediastinum. Mediastinoscopy and sampling of the lesion was inconclusive. F-18 FDG PET/CT done for further characterization of mass detected FDG avid lesion in the right sided chest wall nearer to mid-line (black arrow) in maximum intensity projection (MIP, A). Axial PET, CT and fused PET/CT images (B-D) shows FDG avid heterogeneously enhancing soft tissue mass (white arrow) with central necrosis in the right paratracheal location.
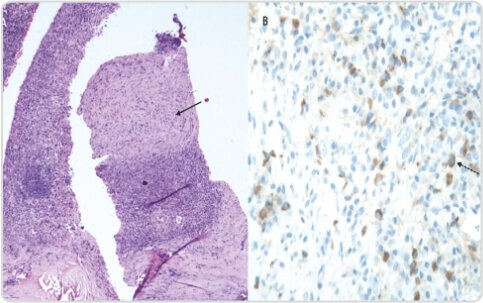
Patient was subjected to PET/CT guided biopsy from the FDG avid lesion. (A) Photomicrograph from the mass revealed mature IgG4+ staining plasma cell infiltrate with interspersed areas of hyalinisation and focal storiform fibrosis (Solid arrow) (B) On IgG4 immunostaining, there were 30-40 IgG4 positive plasma cells (Dashed arrow) per high power field. Brown = cytoplasm of plasma cells containing IgG4, blue = plasma cell nuclei.
Discussion
IgG4 related disease (IgG4-RD) is an emerging clinic-pathologic entity characterized by IgG4 positive plasma cell fibro-inflammatory infiltrates in various organs often supported by elevated serum IgG4 antibodies. Even though IgG4 positive plasma cells are present in various inflammatory lesions, presence of dense IgG4 plasma cell infiltrate > 10 cell/ high power microscopic field is strongly suggestive of IgG4-RD as seen in our case.This disease is often found incidentally as in the index case and those symptomatic, usually present with low grade fever associated with elevated C-reactive proteins. IgG4-RD of pancreas was initially thought to be autoimmune sclerosing pancreatitis associated with elevated serum IgG4 levels.
It is stated that IgG4 RD is a systemic entity and autoimmune pancreatitis is only part of its spectrum. Later, IgG4-RD similar to pancreatic involvement has been reported in many other extra pancreatic organs with bile ducts, salivary glands, lacrimal glands, gall bladder, lymph nodes and retroperitoneum being the most commonly reported organs. Recently, IgG4-RD has also been diagnosed in the prostate gland, testicles, meninges and pituitary gland.
Conclusion
The present case illustrates another rare presentation of this disease in an isolated mediastinal mass on FDG PET/CT and emphasize the importance of biopsy from hypermetabolic site. Clinicians should be aware of the rare presentation of this entity as it is easily treated by steroids and avoids unnecessary surgical procedures.
About Author –
Dr. Kousik Vankadari
DNB, S.R (PGIMER)
Consultant & Nuclear Medicine-PET CT
Yashoda Hospitals, Secunderabad





 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More

