Endoscopic Removal of Foreign Body Case-2
Background
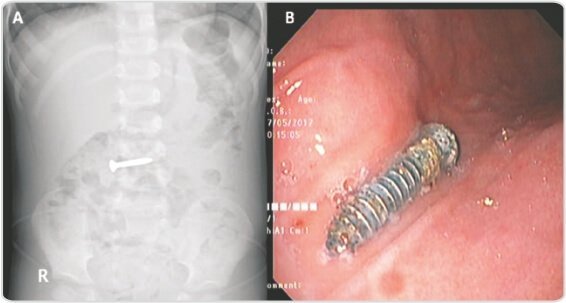
A 3-year-old child presented to us 6 hours after ingestion of a sharp screw.
Diagnosis and Treatment
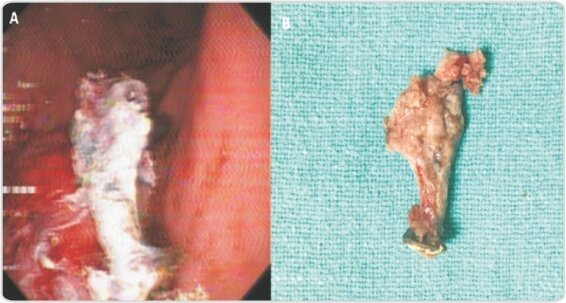
Abdominal X-Ray revealed the screw in duodenum. On endoscopy, the screw was identified in the second part of duodenum. It was repositioned into the stomach using a snare. Subsequently, it was retrieved following a similar technique and steps after applying glue.
Discussion
Existing guidelines recommends the use of protective devices like overtube, transparent cap or latex rubber hood to prevent esophageal wall trauma for endoscopic retrieval of sharp, pointed foreign bodies (1-4). However, overtubes are of larger diameter 19-20 mm and their application and safety in children are not known.
Our technique averted severe trauma to esophagus and, possibly, surgery for the 3-year old index patient who had ingested a screw with sharp edges. Glue, n- butyl 2 cyanoacrylate, polymerizes after contact with weak bases that are commonly used for variceal obliteration and closure of fistulae(5). Our technique is a safe alternative in specific cases of sharp foreign body retrieval.
About Author –
Dr. G. R. Srinivas Rao, Consultant Gastroenterologist, Yashoda Hospital, Hyderabad
DM, MD (Gastro)
About Author
About Author –
Dr. Viswanath Reddy, Consultant Gastroenterologist, Yashoda Hospital, Hyderabad
MD, DM (Gastro)
About Author
About Author –
Dr. B. Ravi Shankar, Consultant Medical Gastroenterologist, Yashoda Hospital, Hyderabad
MD, DNB, DM (Gastroenterology)
About Author
About Author –
Dr. Bharani
MDDM (Gastro)








 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More

