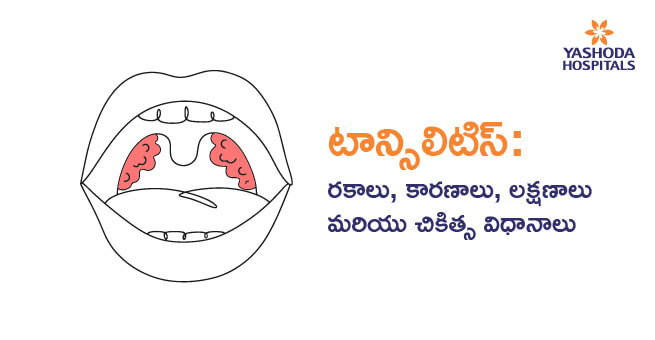
Tonsillar Health: A Detailed Exploration of Tonsillitis, Tonsil Stones, and Related Conditions
Tonsils are those generally tiny, almond-shaped tissues at the back of the throat; they do the work for the immune system mostly during childhood. Oftentimes, however, they become problems, leading to conditions like tonsillitis and tonsil stones. Knowing the symptoms, causes, and treatment of tonsillitis and tonsil stones makes one take care of their throat health.
1. Understanding the Role of Tonsils and its Inflammation and Infection
Tonsils, as guardians at the entrance of the throat, are an essential part of functioning as part of the lymphatic system, an advanced defensive system of the body. Their main role is to serve as a first line of defense against the immune system, with specialized immune cells that carefully trap and inactivate invading pathogens, including bacteria and viruses, that try to enter the body via the oral and nasal cavities. This defensive function is most highly developed during childhood. During prime vulnerability, the immune system is maturing and learning to identify and defend against various potential enemies. Yet, when these protectors themselves become overburdened with infection, they die from inflammation, leading to tonsillitis, an illness defined by inflammation and irritation of the tonsillar tissue, most commonly provoked by either a viral or bacterial invasion.
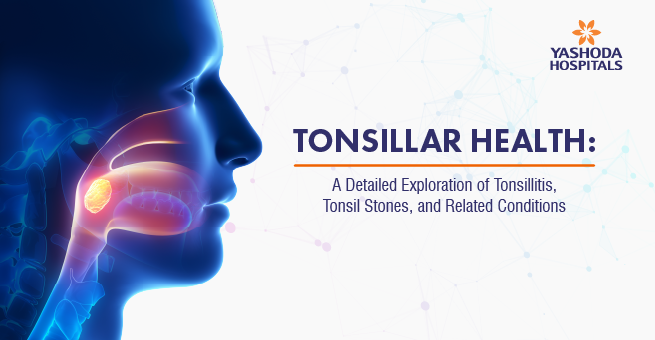
Symptoms of Tonsillitis
Tonsillitis, the inflammation of the tonsils, brings about a variety of symptoms, all of which are a reflection of the body’s mechanism of fighting off the infectious agent. The symptoms show variation in intensity, but those commonly observed are:
- Sore Throat: This is characteristically an extremely sore throat, which may or may not be accompanied by a sensation of scratchiness that goes all the way to the ear or burning pain. Inflammation and irritation of the tonsillar tissue yield a lot of discomfort that goes from making it hard to swallow to an outright inability to do so. One can also notice that speaking and swallowing may bring more pain to the tonsil area.
- Difficulty Swallowing (Dysphagia): The swollen tonsils and surrounding inflammation create a physical obstruction and heightened sensitivity, causing discomfort during deglutition.
- White or Yellowish Patches on the Tonsils: This indicates a bacterial infection, usually streptococcal (strep throat). The patches are made up of pus and cellular debris due to the war being waged by the body against the bacterial invader.
- Visibly Red and Swollen Tonsils: The redness and swelling of the tonsils due to this inflammatory response is caused by increased blood flow and the presence of excess fluid in the tonsils.
- Fever: The core temperature is raised by the body’s immune system to create an environment unlikely to be tolerated by any invading pathogen.
- Headache: These headaches can be triggered by systemic inflammation and the general response of the body to an infection and are usually accompanied by a sense of malaise.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes in the Neck: Due to their activity in inhibiting and filtering out the invading pathogen, lymph nodes drain in response to infection and inflammation in the neck area.
- Earache: Due to the proximity of the tonsils and the ear canals, an inflammatory process in the tonsils may directly cause pain in the ears.
- Bad Breath (Halitosis): This is caused by the infection and debris. The bacterial activity and collection of cellular debris within tonsillar crypts lead to an unpleasant odor.
Stop suffering from tonsil pain.
Causes of Tonsillitis
Tonsillitis used to be defined as an infectious and inflammatory disease of the tonsils originating from infectious agents penetrating the throat. Most of the agents may be classified in this way, and each agent is known to elicit a particular immune reaction:
- Viral Infections: Many viruses can induce tonsillitis; rhinoviruses, influenza viruses, and adenoviruses can also cause tonsillitis. These refer to more generalized upper respiratory infections that might manifest with tonsillitis as one of the symptoms. The immune system’s response to viral invasion includes inflammation; hence, the swelling and redness of the tonsils occur.
- Bacterial Infections: Streptococcus pyogenes is the most commonly known bacterium responsible for causing tonsillitis and strep throat. It additionally tends to have more severe symptoms, such as a severe sore throat, white or yellow deposits on the tonsils, and fever. The safety is triggered by this bacterium, which brings out a very vigorous immune response and pus formation with a lot of swelling in the tonsillar tissue.
Diagnosis of Tonsillitis
Diagnosing tonsillitis involves a visual assessment and laboratory testing to pinpoint the root cause of inflammation.
- Examination by a Doctor: The doctor is likely to conduct a visual inspection of the throat and tonsils and consider whether any signs of inflammation are present, such as redness, swelling, or white or yellow patches. Next, they will palpate the lymph nodes over the neck for signs of tenderness and enlargement as an indication of an active immune response to the infection. The ears and nose, as well as other sections of the upper respiratory tract, may be examined to exclude another mechanism behind the symptoms.
- Throat Swab: A throat swab is used to find out whether a case of streptococcal infection, meaning Streptococcus pyogenes, is causing it, particularly strep throat. A sample of secretions is taken from the surfaces of the tonsils and the back of the throat using a sterile cotton swab gently pressed against the two surfaces. The sample is then tested in one of two ways:
- Rapid Strep Test: Results will be available immediately after a few minutes since the presence of strep bacteria is detected.
- Culturing Throat: Culturing in the laboratory of the bacteria either 24 hours to 48 hours provides a more definitive diagnosis and isolates different possible pathogenic bacteria.
Treatment of Tonsillitis
Tonsillitis has different approaches to alleviating symptoms and treating the underlying infection depending on whether it is viral or bacterial:
- Viral tonsillitis: Viral tonsillitis is a self-limiting condition where the body fights off the infection without medication. Hence, it is of utmost importance to get good rest through sleep or staying away from activities that are strenuous in any way so that energy can be directed toward fighting the active infections. Any healthy fluids one may take on board, such as water, herbal teas, and clear broths, would also serve the purpose of preventing dehydration and the further aggravation of symptoms like sore throat and fever. Acetaminophen and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents available without prescription can come in handy for reducing fever, relieving pain, and providing comfort. Surgical removal of the tonsils (tonsillectomy) is considered for severe or recurrent tonsil infection.
- Bacterial tonsillitis: Bacterial tonsillitis, a type of strep throat, requires antibiotic treatment to prevent complications like rheumatic fever or peritonsillar abscess. The correct antibiotic, typically penicillins or cephalosporins, will be prescribed by a physician after diagnosis. Make sure to complete the total course of antibiotics prescribed, even if one feels a lot better, to prevent the risk of developing antibiotic resistance. Surgical removal of the tonsils (tonsillectomy) is considered for severe or recurrent tonsil infection.
Considering Tonsillectomy?
Tonsil Stones (Tonsilloliths): Trapped Debris
Tonsil stones, or tonsilloliths, are small, hardened masses that form in the recesses and crannies (crypts) of tonsillar tissue. These formations can be considered waste since they are incidental products of the tonsils’ normal work of filtering and trapping foreign materials. Tonsil stones are composed of some mixture of:
- Bacteria: Various strains of bacteria in the oral cavity are trapped within the tonsillar crypts, where they aid in the formation and composition of the stones.
- Dead Cells: Desquamated epithelial cells from the tonsils and adjacent tissue surfaces contribute a major share of this debris.
- Mucus: These secretions from the mucous membranes in the throat fill in the sticky matrix that binds the other components.
- Food Debris: Small bits of food trapped in the tonsillar crypts furnish a medium for bacterial multiplication while contributing to the overall mass of the stone.
- Calcified Deposits: With time, this waste material becomes calcified, meaning minerals like calcium and phosphorus are laid down in the debris, resulting in the hardened stone character of the tonsilloliths.
What Causes Tonsil Stones?
- Tonsil Crypts: The uneven tonsil surface containing crypts provides an ideal space for debris accumulation.
- Bacteria and Debris: Bacteria and debris become trapped within the crypts and eventually harden.
- Chronic Tonsillitis: Recurrent tonsil infections may raise the risk of tonsil stones.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Poor oral hygiene may lead to the accumulation of debris.
Tonsil Stone Symptoms
Symptoms of tonsilloliths include:
- Bad Breath (Halitosis): A frequent symptom caused by bacterial accumulation. The debris trapped in the tonsil crypts promotes bacterial growth, resulting in the release of volatile sulfur compounds that produce chronic bad breath.
- Sore Throat: Pain or irritation in the throat. Tonsil stones may produce a scratchy or irritated sensation, especially when swallowing, due to the physical presence of the stones and related inflammation.
- Difficulty Swallowing: A sense of something stuck in the throat. The physical presence of larger tonsil stones can cause a sense of blockage, with swallowing being uncomfortable or difficult.
- White or Yellow Lumps on Tonsils: Stones seen on the surface of the tonsils. These are the calcified deposits themselves, small whitish or yellowish lumps trapped in the tonsillar crypts.
- Ear Pain: The tonsils’ location close to the ear canals can on occasion lead to referred pain, when pain is experienced in the ears when the cause lies in the tonsils.
- Metallic Taste: Bacterial activity and tonsil stone composition can at times cause a persistent metallic or unpleasant taste.
Tonsil Stone Treatments
Tonsil stones, though usually harmless, may be painful and lead to bad breath. Several treatments exist, from basic home remedies to surgery, depending on the severity and frequency of the occurrence.
- Gargling: Gargling with warm salt water may dislodge small stones. Salt water is a mild antiseptic, and the pressure of gargling can physically dislodge loose tonsil stones.
- Manual Extraction: Gently using a cotton swab or oral irrigator to remove the stones that can be seen. It is necessary to be cautious not to cause injury to the tonsil tissue, and it is most effective for stones that are easily reachable.
- Coughing: At times, stones may be dislodged by coughing. The pressure from a severe cough can at times dislodge loosely impacted stones within the tonsillar crypts.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics can be prescribed in the event of infection. If the tonsil stones are linked to a bacterial tonsillitis infection, antibiotics are employed to eliminate the infection but not the stones themselves.
- Tonsillectomy: Surgical removal of the tonsils may be considered for very bad or frequent tonsil stones. This is more aggressive and reserved for when other therapies have not worked and the stones are truly creating a lot of trouble.
- Laser Tonsil Cryptolysis: A laser surgery that flattens the tonsil surface, eliminating crypts. This surgery is done to decrease the number of crypts where debris can settle, thus avoiding the development of tonsil stones.
Worried About Tonsil Stones or Frequent Infections?
Can Tonsils Grow Back?
It is a common question whether the tonsils can regrow after tonsillectomy, and it depends on the type of operation done. Here are the distinctions:
- Partial Tonsillectomy: If only part of the tonsils is removed, some regeneration can occur in the remaining tissue. This means that the remaining tonsil tissue might enlarge, but this is not a true regrowth of the original tonsils.
- Complete Tonsillectomy: There is no possibility of regrowth after a complete tonsillectomy, where all the tonsil tissues have been removed. Lymphatic tissue could grow around the area, but it won’t fill in for the tonsils. This tissue is, of course, involved in the immune response, but it does not perform any of the functions activated by the original tonsils.
- Ectopic Tonsil Tissue: It is possible, though rare, for ectopic tonsil tissue to appear in unusual locations, such as on the tongue base or the posterior pharynx, but this is not considered regrowth. Ectopic tissue is simply a developmental anomaly and is not regeneration of previously removed tonsils.
When to See a Doctor?
Immediately seek medical assistance if one experiences:
- Severe Sore Throat
- Persistent Tonsil Stones
- Recurrent Tonsillitis
- Breathing Difficulties
- Suspicion of Strep Throat
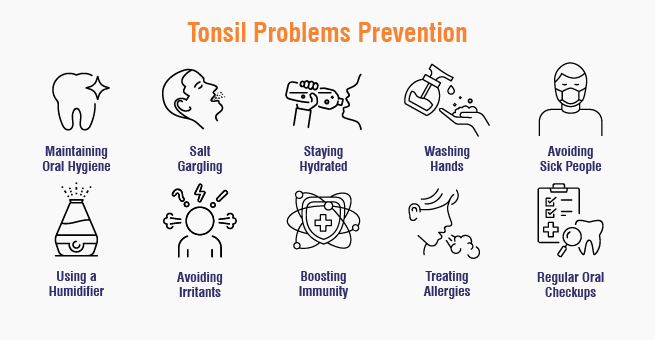
Preventing Tonsil Problems
The following are some of the proactive measures that make it possible to keep one’s tonsils healthy:
- Keep Good Oral Hygiene: Preferably, brush at least twice a day, floss daily, and rinse with antiseptic mouthwash after brushing to destroy bacterial buildup.
- Hydration: Drinking lots of water throughout the day can keep the throat from drying and help flush debris out.
- Wash Hands Regularly: Regular hand washing minimizes the chances of contracting viral and bacteria-leading diseases of the throat, such as tonsillitis.
- Avoid Close Contact with Sick People: Stay clear from such people who are having an upper respiratory infection, as they can transfer the infection to you.
- Salt Water Gargle: Gargling warm salt water will help cleanse and reduce inflammation of the tonsils.
- Use a Humidifier: Adding moisture to the air prevents dryness and irritation of the throat, especially during dry seasons.
- Minimize Exposure to Irritants: Prevent smoking, secondhand smoke, and any other airborne irritants that can inflame the tonsils.
- Boost the Immune System: A well-balanced diet containing fruits and vegetables along with the right exercise at the appropriate time can give one more sleep and a healthier diet.
- Treat the Allergies: If one suffers from allergies, treat and manage them such that they cannot cause throat irritation or problems in the tonsils.
- Regular dental checkup: Be sure to continue having regular dental checkups because oral health directly corresponds to the well-being of the tonsils.
Living Without Tonsils
Thousands of people live their day-to-day lives without their tonsils. The immune system does possess other means and mechanisms, however, to fight infection. There are some very few people who are prone to having a slightly higher risk of suffering from specific infections in the first couple of years following tonsillectomy.
Conclusion
The tonsils, though small in size, have an important impact on our immune health. Knowing the symptoms that come with tonsillitis, understanding the causes of tonsil stones, the treatments for them, and when to seek a doctor’s help will help you know how best to keep your throat in optimal health. With care and good hygiene, you can keep your tonsils healthy and operating well. In case of recurring or pronounced problems with your tonsils, it would always be best to visit your doctor.
Yashoda Hospitals offers extensive treatment of tonsil ailments, such as tonsillitis, tonsil stones, and other throat ailments, in its specialized ENT (ear, nose, and throat) centers. Its qualified otolaryngologists, ENT surgeons, and specialists provide a variety of diagnostic and therapeutic options, from medical treatment of infections with antibiotics and supportive management to advanced surgeries such as tonsillectomy and laser tonsil cryptolysis for persistent or severe conditions. They stress patient-centric care, assuring precise diagnosis, tailored treatment options, and extensive post-surgery care, making use of cutting-edge technology and infrastructure to treat different throat afflictions efficiently.
Have any questions or concerns about your health? We’re here to help! Call us at +918929967127 for expert advice and support.












 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More

