Is Spine Surgery Safe? Exploring Minimally Invasive Techniques and Recovery
Spine surgery is a source of fear for most people, yet it has undergone significant improvements. These new techniques aim at minimally invasive procedures that will ensure safety and less disruption of the patient. Modern approaches consider smaller incisions, less damage to muscles, and faster recovery compared to open traditional surgery. The safety aspects of spine surgery will be explored in detail, focusing on minimally invasive procedures and what patients can expect during the recovery process.
Understanding Spine Surgery
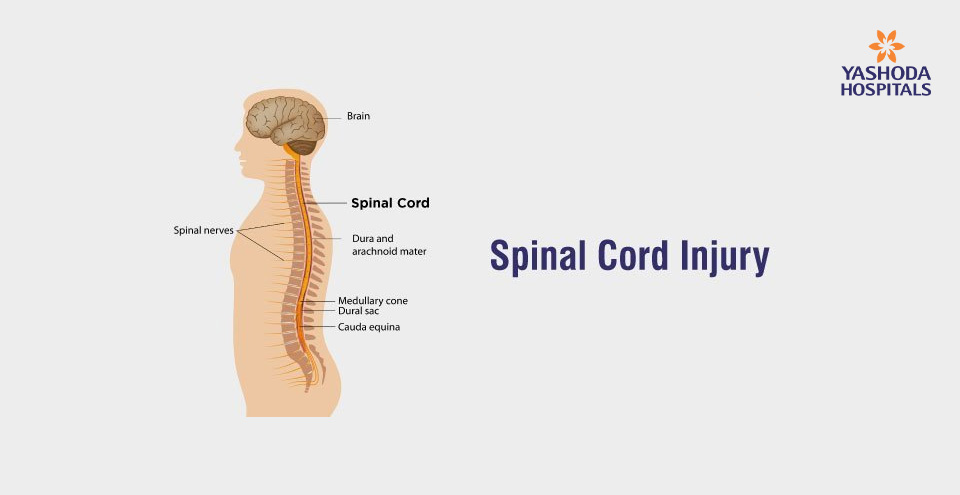
Spine surgery is one of the medical practices used after other non-surgical treatments such as physical therapy, medication, and injections have failed to deliver sufficient relief from back or neck pain. Its objectives focus on pain relief, improved function, and stabilization of the spine. In addition, the restoration of daily activities by improving function and prevention of further damage or deformity make spinal stability. Vertebral fractures, spondylolisthesis, or scoliosis may sometimes require surgery. With these, spine surgery profoundly improves the quality of life for a patient, improving his/her overall well-being.
Spine surgery includes a variety of techniques such as discectomy, laminectomy, spinal fusion, and vertebroplasty/kyphoplasty. Minimally invasive techniques have improved with smaller incisions, less tissue damage, and faster recovery times. Spine surgery can improve quality of life, but one should seek a qualified surgeon to determine the best course of treatment based on individual needs and circumstances.
Types of Spine Surgery
Some of the most common types of spine surgeries are detailed as follows:
- Discectomy (Microdiscectomy): Microdiscectomy is a method through which a compressed nerve root with a herniated or budging disc is removed through the utilization of specialized tools and a small incision for treating herniated discs, sciatica, and nerve pain.
- Laminectomy/Laminotomy: This is a procedure undertaken to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots due to spinal stenosis. It involves removing the entire lamina. But in a laminotomy, only a portion is removed. This procedure treats spinal stenosis, back pain, leg pain, and neurogenic classification symptoms.
- Spinal Fusion: This procedure is defined as the one through which two or more vertebrae are fused into a solid unit, eliminating movement between them, thereby making the bones stable. A bone graft is then inserted between these vertebrae with the necessary hardware to stabilize them together. The process has been proven to be beneficial in spondylolisthesis, scoliosis, spinal instability, and degenerative disc disease.
- Vertebroplasty/kyphoplasty: Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty are minimally invasive procedures used to treat vertebral compression fractures, which are most commonly caused by osteoporosis. These fractures weaken and collapse the spine, causing pain and deformity. Both procedures inject a special cement into the fractured vertebra, with kyphoplasty using a balloon to create space before injecting cement, restoring lost height and improving spinal alignment.
- Artificial Disc Replacement: It is a surgical procedure where a damaged or degenerated disc in the spine is removed and replaced with an artificial disc. The artificial disc is made to mimic the motion and function of the original disc, allowing the spine to continue moving and staying flexible.
- Foraminotomy: Foraminotomy surgery is performed to enlarge openings in the spine where nerves exit such openings called foramina. These foramina can become narrow or stenotic and thereby compress or pinch the nerves, causing pain, numbness, or weakness. Foraminotomy alleviates this pressure by making room for nerves to pass through.
In addition to the above discussed, there are a few more types of spine surgeries recommended to the patients based on their condition. In general, spine surgeries are performed in the lumbar and cervical regions based on the patient’s condition and the affected sites.
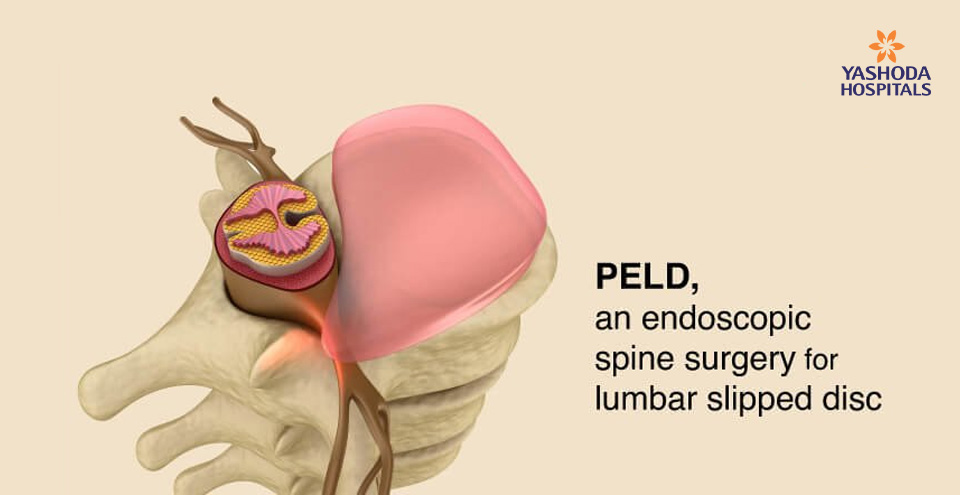
Lumbar spine surgery addresses lower back problems: the herniated disks, spinal stenosis, spondylolisthesis, and degenerative disk disease. Typical lumbar spine surgical procedures include laminectomy, discectomy, spinal fusion, and minimally invasive procedures such as microdiscectomy and percutaneous endoscopic discectomy. The purpose of these surgeries is to relieve pressure on nerves, remove herniated disks, stabilize the spine, and minimize tissue disruption.
Whereas cervical spine surgery is neck surgery that addresses cervical disc disease, disc herniation, stenosis, neck pain, or radiculopathy. Common procedures that are performed are the cervical laminectomy, anterior cervical discectomy, and fusion (ACDF), along with other procedures that will serve to enlarge the exits in your spine through which nerves exit from the spinal cavity.
Approaches to Spine Surgery
The various approaches to spine surgery are done with the use of different methods and have their respective advantages and disadvantages. They include open surgery, minimally invasive techniques like endoscopic surgery, robot-assisted procedures, and more. The approach will be determined by factors such as the specific condition, the surgeon’s expertise, and the patient’s overall health. The approaches are discussed in detail as follows:
- Open spine surgery: It is a conventional approach in spinal operations; an open spine procedure; a large incision is done, and it will allow access to the spine directly, thus permitting visualization and manipulation of spinal structures. All these are necessary for extensive procedures: spinal fusions, tumor removals, severe trauma cases, and so on. Open surgery, however, usually incurs more extensive muscle dissection and therefore larger scars, longer recovery times, and higher complication rates than minimally invasive techniques.
- Minimally invasive spine surgery: Minimally invasive spine surgery has probably always been the biggest enter in modern spinal care because it’s supposed to offer benefits that open surgery just doesn’t. The “minimally invasive” techniques involve smaller incision sizes, specific targeting instruments, and modern techniques to treat problems such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or other tumors from the spinal column. Techniques utilized include microdiscectomy and percutaneous spinal endoscopic discectomy (PECS), reducing muscle disruption and blood loss, with shorter recovery times than an open surgery.
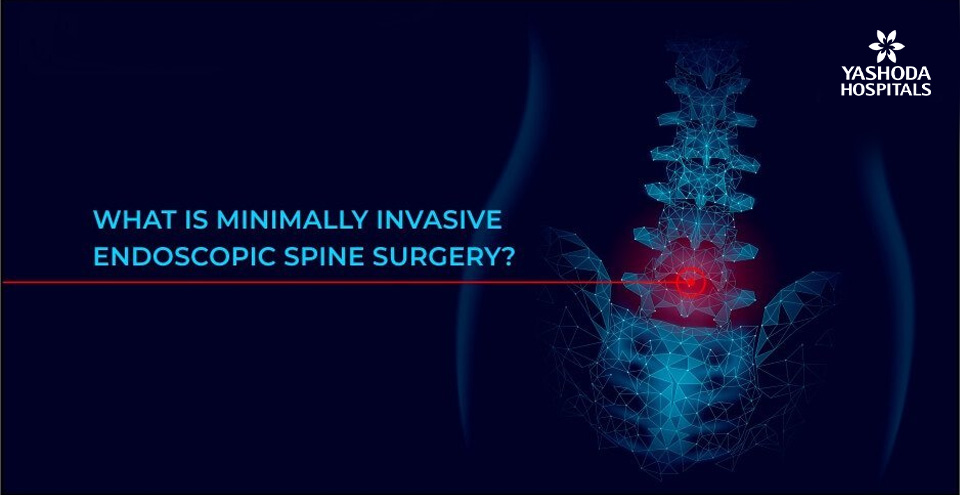
- Endoscopic spine surgery: Endoscopic spine surgery is a procedure that can be defined as minimally invasive as it consists of small incisions and special instruments to treat various conditions around the spine. In this procedure, a thin tube with a camera and light source is inserted through a small incision, which will be seen on a monitor by the surgeons. This technique has advantages in terms of pain, recovery time, and inpatient hospitalization compared to traditional open surgery and is restricted to certain conditions.
- Robot-assisted spine surgery: Assisted by robot technology, robot-assisted spine surgery provides more precise, accurate, and flexible ways of performing spinal procedures compared to a surgeon working entirely with the traditional methods. It serves as an extension of the surgeon’s hands, translating their movements into accurate robotic movements to gain control and maneuverability in complex cases. And when coupled with minimally invasive techniques, it can lead to better surgical outcomes with associated complications being reduced.
- Laser spine surgery: It is a minimally invasive, laser-assisted procedure to remove or reshape spinal tissue in treating conditions like herniated discs, stenosis of the spine, and facet joint syndrome. The laser can precisely target and remove diseased tissue, thus minimizing damage to surrounding structures.
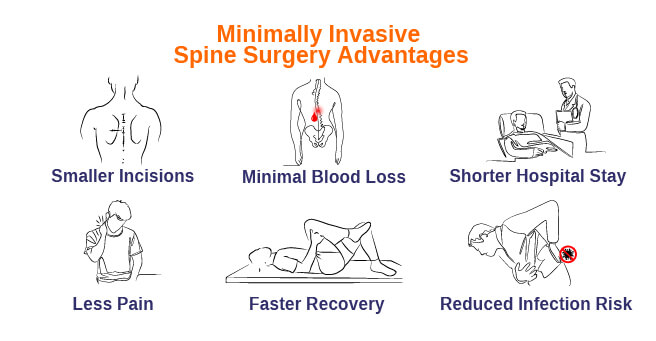
Advantages of Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery
Advantages of minimally invasive spine surgery (MISS) over traditional open spinal surgery include:
- MISS utilizes smaller incisions, resulting in less traumatic effects on muscle and tissues.
- The amount of blood loss during MISS procedures will generally be less.
- Patient experience shorter hospitalization.
- Much less damage to muscles leads to less pain and, most of the time, early recovery and return to normal activity.
- Postoperative pain is less when compared to other alternatives.
- Improved cosmetic outcomes
- Infection risk will be less due to less scarring.
Recovery from Spine Surgery
Recovery time following spine surgery is individual and varies between procedures, with the overall condition of the patient’s health and extent of surgery as contributing factors. Open spine surgeries have longer recovery times due to larger incisions and potential damage to muscle tissues and possibly tissues involved. Pain control may need more potent medications, and patients take several weeks to months before getting back to regular activities. Typically, they will have to go through physical therapy for strength, flexibility, and movement.
MISS has a better recovery time by minimizing the time due to fewer incisions, low tissue trauma, and lessened blood loss during surgery. Oftentimes, pain management requires reduced amounts of pain medications and helps in the earlier return of the patient’s normal activities. The time of recovery can be as soon as a few days or weeks using endoscopic spinal surgery with minimal utilization of pain medicine. However, recovery time might be altered due to the patient’s overall health, age, post-operative care, and complications in some cases.
Recommended with any of the above surgery?
When to Seek Appointment from Doctor?
One should consider scheduling an appointment with a spine specialist (such as a neurosurgeon or orthopedic spine surgeon) if one experiences any of the following:
- Chronic back pain or neck pain that persists for 12 weeks or longer despite conservative treatments like physical therapy, pain medication, and rest.
- Intrusive pain that significantly interferes with daily activities, such as work, sleep, or leisure.
- Weakness, numbness, or tingling in an arm or a leg.
- An abrupt loss of bladder or bowel control.
- Progressive loss of strength.
- Acute or severe pain, especially following trauma.
- Failure of nonsurgical treatment to alleviate symptoms adequately.
Conclusion
Spine surgery is a major medical procedure aimed at relieving pain and restoring function and quality of life in patients with spinal diseases. Although great strides have been taken in surgical technique, the point should not be lost that each case is unique.
Yashoda Hospitals is a well-known health care provider with a long history of excellence in spine care. Our spine surgeons are highly experienced and utilize the latest techniques and technologies to treat a wide range of spinal conditions, including herniated discs, spinal stenosis, and spinal tumors.
Have any questions or concerns about your health? We’re here to help! Call us at 918065906165 for expert advice and support.














 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More