From Laparoscopy to Robotics: The Evolution of Minimally Invasive Surgery

1. What is Minimally Invasive Surgery?
Minimally invasive surgical procedures are carried out by small openings instead of making large incisions, leading to benefits for the patient in reduced pain, smaller scars, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times. Instead, this type of surgery used special instruments—endoscopes, laparoscopes, and robotic systems—to visualize and manipulate internal organs and tissues more closely, avoiding extensive disruption. Different surgical specialties apply it to. Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and advanced imaging bring new promises to MIS for improved precision, extended opportunities for procedures, and personalized interventions.
Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) represents one of the most advanced surgical techniques, as it is less traumatic compared to traditional open surgery. Increasingly, in less invasive interventions, MIS is rapidly becoming the go-to approach across specialties and for more procedures. While there are clearly many advantages to MIS, one must always keep in mind that not all surgical procedures lend themselves to minimally invasive techniques. Whether an operation falls into this category or not is a decision by a surgeon based on various factors such as the specific condition of the patient, the general health of the patient, and so on. MIS also requires special training and expertise from the surgeon involved in such a procedure to perform it successfully.
2. Understanding Minimally Invasive Techniques
A. Laparoscopic Surgery: Precision Through Small Incisions
- The laparoscope is a new-age instrument as thin as a pencil with a camera at one end. Laparoscopic surgery is done through a few small incisions that allow high-definition and magnified images of the internal surroundings, where the surgeon can carefully perform complex procedures in a minimally disruptive way.
- The advantages of laparoscopy over open surgery include:
– Lesser pain after surgery
– Small scars and lesser blood loss
– Shorter hospital stay and quicker recovery
– Reduced likelihood of infection - Some of the most common laparoscopic procedures include cholecystectomy (gallbladder removal), appendectomy, hernia repair, colon surgery, hysterectomy, nephrectomy, and surgeries for bariatric problems, including gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy. These procedures are done for treating gallstones, hernias, appendicitis, endometriosis, and some cancers
B. Endoscopic Surgery: Accessing the Body’s Interior
Endoscopic surgery consists of passing a thin, flexible tube with a camera (endoscope) through natural orifices like the mouth, nose, or urethra. This method provides real-time visualization and minimally invasive repair of internal organs.
- Upper endoscopy evaluates the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum.
- Colonoscopy is employed to examine the colon for any abnormalities.
- Bronchoscopy aids in visualizing the airways and diagnosing lung disorders.
C. Robotic Surgery: The Future of Precision Medicine
- Robotic surgery uses a surgical robot controlled by the surgeon to perform the operation from a console and then takes it a step further because of the added precision, dexterity, and visualization the robot provides, especially when it comes to complex cases. Besides, robotic surgery is applied across several specialty areas, including urology (prostate surgery), gynecology (hysterectomy), and cardiac surgery.
- The Da Vinci Robotic Surgery is an advanced robotic platform used in minimally invasive surgery. It includes a surgeon console, patient cart with interactive robotic arms, and a high-definition 3D vision system. The Da Vinci robot mimics the surgeon’s hand movements, providing precision, control, and visualization, even in tight areas.
- Quite recently, advances have been made in robotic-assisted surgery. Currently, advances include thoracoscopy, laparoscopy, gynecology, urology, and any minimally invasive procedure. Robotic systems have also developed over the years and are well-suited for emergency surgery.
- Advantages of robotic surgery include enhanced precision, improved visualization, greater dexterity, smaller incisions, reduced blood loss, shorter hospital stays, faster recovery, and less noticeable scarring. Its 3D, high-definition vision system provides a superior view of the surgical field, improving surgical outcomes. Robotic surgery also allows for smaller incisions, reducing pain, scarring, and infection risk. Further research is ongoing to explore potential improvements in clinical outcomes.
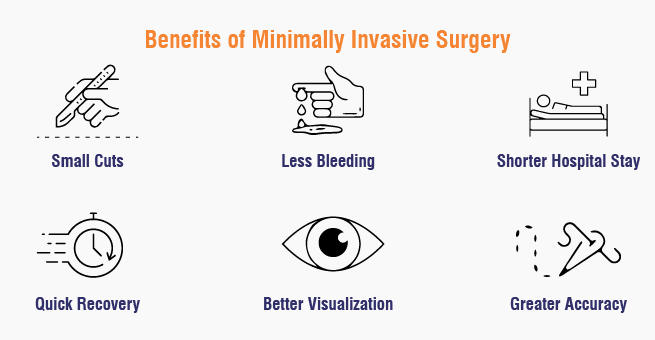
3. Why Should One Opt for Minimally Invasive Surgery?
The following are some of the common reasons why someone might opt for minimally invasive surgery (MIS):
- Small Cuts, Less Pain: MIS uses tiny openings in the abdomen, thereby causing low to significantly lower pain after surgery than what is expected from normally open surgeries.
- Minimal Scarring: Incisions of such a small size would heal into very tiny, almost invisible scars, such that even the cosmetic results would be better.
- Lower Bleeding: Minimally invasive procedures usually involve the least blood loss during the process, which reduces the need for a blood transfusion.
- Shorter Hospital Stay: Compared to open procedures, patients could end up going home on the same day when they undergo surgery instead of staying for days.
- Shorter Duration of Recovery: Recovery usually takes place faster, leading to the patients getting back to their normal activities and working much sooner.
- Lower Rate of Infection: A wound incision is a very small area; hence, there is a lower risk for infection developing as opposed to most wounds from open surgeries.
- Less Trauma to Tissues: Less damage occurs to surrounding tissues and organs with minimized risk.
- Better Visualization: The surgeon would have seen the surgical field with much greater detail and clarity due to laparoscopes or robotic systems providing a magnified view.
- Greater Precision: Robotic surgery provides especially better precision and flexibility of movement, making the performance of complex maneuvers more accurate by the surgeon.
- Potential for Better Outcomes: By most definitions, for many conditions, MIS has been associated with improved clinical outcomes, which include the reduced incidence of complications, less pain, and faster return to function.
4. The Future of Minimally Invasive Surgery: Emerging Technologies and Potential Advancements.
Technological innovations will see substantial advances in the future of minimally invasive surgery (MIS). Artificial intelligence and machine learning will allow surgeons to analyze data in real time for planning and decision-making. Advanced imaging techniques (augmented reality and 3D visualization) will improve accuracy. Robotics will develop further to enhance freedom and flexibility. New energy options and surgical instruments will take MIS techniques to the next level. Personalized medicine will be emphasized. Patient-specific approaches will be crafted using data from medical imaging and genomics to generate customized plans. Education and engagement of patients will be enhanced through the use of virtual reality and simulation technology.
5. Comparing Surgical Approaches
Robotic Surgery vs. Laparoscopic Surgery:
Minimally invasive, robotic surgery differs from laparoscopic surgery in the way that the surgeon interacts with the surgical field. In laparoscopic surgery, long, thin instruments are manipulated through small incisions, with surgery largely dependent on the dexterity of the surgeon and limited to a two-dimensional view from the laparoscope. For robotic surgery, the surgeon controls the robotic system, which translates hand movements into precise movements of specialized arms. This system also provides a magnified three-dimensional view of the surgical field, enhancing depth perception. Ultimately, the choice between robotic and laparoscopic techniques will hinge on the procedure in question, the surgeon’s expertise, and available resources.
Robotic Surgery vs. Open Surgery:
Robotic surgery is a very effective alternative to open surgeries that usually involve large incisions and require retraction of extensive tissue, resulting in patients suffering increased postoperative pain, longer hospital stays, and longer recovery. Robotic surgery makes use of small incisions and precise instrumentation to effectively minimize tissue trauma and risks associated with large incision surgery. Consequently, robotic surgery typically leads to less blood loss, smaller scars, reduced pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times. However, one of the most significant advantages that robotic surgery has improved visualization and dexterity and, therefore, is preferred over many procedures.
Laparoscopic Surgery vs. Endoscopic Surgery:
In laparoscopic and endoscopic surgery, access to different parts of the body’s interiors is minimally traumatic. Typically, laparoscopic surgery, intended for use in the abdominal cavity, involves using small incisions to introduce instruments and a camera, with procedures of the gallbladder, appendix, and intestines being commonly performed. In contrast, endoscopic surgery may use any natural body openings available to access the internal organs, such as through the mouth, nose, rectum, or urethra. Both techniques require small incisions, and the choice between them depends on the procedure’s location and nature.
Conclusion
The era of minimally invasive surgery has transformed the surgical field, moving from open to laparoscopic and robotic-assisted procedures. This evolution prioritizes patient well-being, offering smaller incisions, reduced pain, faster recovery, and improved outcomes. Advancements in technology, including AI, imaging, and robotics, promise to refine the techniques, pushing the boundaries of surgical possibilities. The future of surgery is moving towards less invasive approaches, offering better patient care and outcomes.
Yashoda Hospitals offers advanced minimally invasive surgical options, including laparoscopic and robotic surgeries using the Da Vinci system. Our team of skilled surgeons uses advanced techniques to deliver the best possible care, minimizing patient discomfort and maximizing recovery speed. We believe in empowering patients with the latest advancements in surgical care, ensuring they receive the most effective and least invasive treatment options available.
Have any questions or concerns about your health? We’re here to help! Call us at +918929967127 for expert advice and support.
Consultant Surgical Gastroenterologist, Laparoscopic, Bariatric & Metabolic Surgeon













 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More

