Managing Diabetes with Insulin Pumps

Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is a common and often misunderstood group of viruses that can lead to a variety of health issues, including skin and mucous membrane infection and certain types of cancers. They are a group of more than 200 related viruses. Human papillomavirus (HPV) causes more than one-fourth of infection-related cancers globally.
According to the National Cancer Registry Programme (NCRP) data, among all the cancers in India, 7.5% of cancers were related to HPV infection. The most common HPV-related cancers in males and females were oropharyngeal cancer (63.2%) and cervical cancer (87.6%), respectively.
Worldwide, the burden of HPV-related cancers is much greater. High-risk HPVs cause about 5% of all cancers worldwide, with an estimated 570,000 women and 60,000 men getting an HPV-related cancer each year. Cervical cancer is among the most common cancers and a leading cause of cancer-related deaths in low- and middle-income countries, where screening tests and treatment of early cervical cell changes are not readily available.
Understanding the Mechanics of Insulin Pumps and CGM sensors
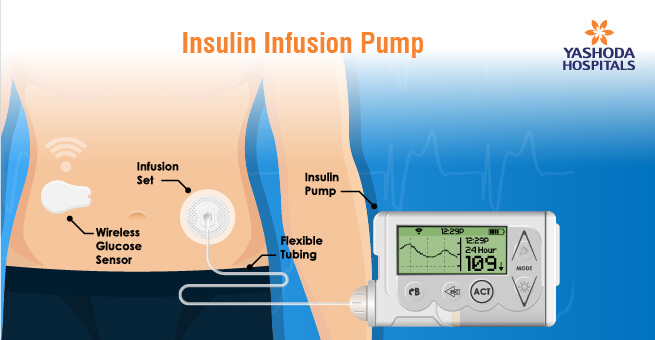
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. For those with Type 1 diabetes or advanced Type 2 diabetes, insulin pumps have revolutionized the way they manage their blood sugar levels. Insulin pumps are small, computerized devices that deliver a continuous supply of insulin into the body. Unlike traditional insulin injections, which require multiple daily shots, insulin pumps offer a more precise and convenient way to manage blood sugar levels.
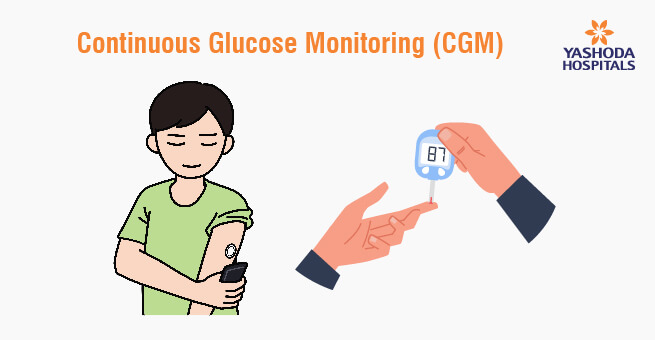
In this dynamic landscape, Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) sensors play an integral role. They provide real-time glucose data, enhancing insulin dosing decisions and reducing the risk of hypoglycemia. The seamless integration of CGM sensors with insulin pumps streamlines diabetes management, improving blood sugar control and overall quality of life. Close collaboration with healthcare providers is essential for maximizing the benefits of both technologies in successful diabetes management.
Highlighting the Omnipod insulin pump which is tubeless, wearable device that adheres to the skin, offering wireless control through a handheld device. It’s waterproof, allows for dosing flexibility, and can integrate with Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) sensors. Its user-friendly design and discretion make it a popular choice for insulin pump therapy without tubing. When considering insulin pumps, explore options like the Omnipod in consultation with your healthcare team.
Ready to revolutionize your diabetes management with insulin pumps? Explore, choose, and transform your health!
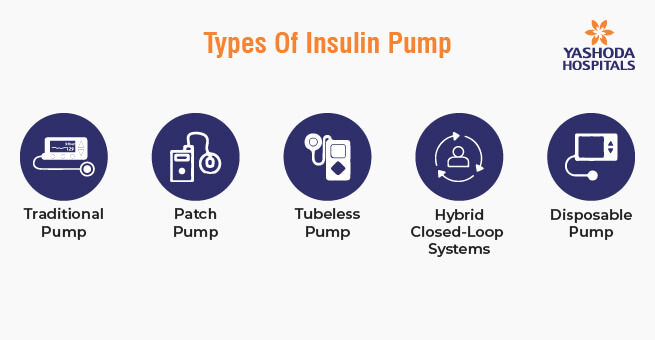
Types of Insulin Pumps
There are several types of insulin pumps available for people with diabetes. These devices are designed to deliver a continuous supply of insulin to help manage blood sugar levels. The specific features and capabilities of insulin pumps may vary by manufacturer and model, but here are some common types:
- Traditional Insulin Pump: This type of pump delivers a continuous basal rate of insulin throughout the day and allows the user to bolus (deliver a larger dose of insulin) for meals and corrections. They typically use rapid-acting insulin and are connected to the body via a small cannula inserted under the skin.
- Patch Pump: Patch pumps are tubeless insulin pumps that adhere directly to the skin. They have a small reservoir of insulin and a cannula for subcutaneous insulin delivery. Users can control them wirelessly through a separate handheld device or a smartphone app.
- Tubeless Insulin Pump: These pumps are similar to traditional pumps but do not have a tubing system. They are more discreet and are often controlled via a wireless remote or smartphone app. Omnipod is a well-known example of a tubeless insulin pump.
- Hybrid Closed-Loop Systems: Some insulin pumps can work in combination with continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) to create a hybrid closed-loop system, also known as an artificial pancreas. These systems can automatically adjust basal insulin delivery based on real-time CGM data to help maintain target blood sugar levels.
- Disposable Insulin Pump: These are usually lower-cost options for those who want to try out insulin pump therapy or need a temporary solution. Disposable pumps are worn for a few days or weeks, depending on the model, and then discarded.
- Integrated Insulin Pump: Some insulin pumps are integrated with a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) in a single device. This integration allows for more seamless insulin management, as the pump can automatically adjust insulin delivery based on CGM data.
- Traditional Insulin Pump with Bluetooth Connectivity: Many modern insulin pumps are equipped with Bluetooth connectivity, allowing users to connect them to smartphones or other devices for remote monitoring and control.
- Mini-Dose Insulin Pump: These insulin pumps are designed for people who require very small doses of insulin, such as children or those with high sensitivity to insulin. They can deliver extremely precise insulin increments.
Benefits of Insulin Pumps
- Improved Blood Sugar Control: Insulin pumps allow for precise insulin delivery, reducing the risk of high and low blood sugar spikes. This can lead to better overall blood sugar control, lowering the risk of diabetes-related complications.
- Flexibility: With an insulin pump, users have more flexibility in their daily routines. They can adjust basal rates and bolus doses to accommodate varying activity levels, meal sizes, and schedules.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: The convenience of insulin pumps can significantly improve the quality of life for people with diabetes. They no longer need to carry syringes and insulin vials, and the discrete nature of the pump allows for more freedom and confidence in social settings.
- Reduced Hypoglycemia Risk: Insulin pumps can help reduce the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) by providing precise insulin dosing and suspending insulin delivery when necessary.
Tips for Effective Insulin Pump Use
- Education: Proper training and education are essential. Work closely with your healthcare team to learn how to use the pump, calculate insulin doses, and manage your diabetes effectively.
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring: Consider using a CGM system in conjunction with your insulin pump. CGM provides real-time data on your blood sugar levels, helping you make informed decisions about insulin dosing.
- Regular Monitoring: Even with an insulin pump, it’s important to monitor your blood sugar levels regularly and adjust your insulin doses as needed.
- Site Rotation: Rotate the infusion site regularly to prevent tissue irritation or insulin absorption issues. Common infusion sites include the abdomen, thighs, and buttocks.
- Emergency Plan: Have a plan in place for handling pump malfunctions or situations where the pump may need to be temporarily disconnected.
Choosing the Right Insulin Pump
Selecting the right insulin pump is essential for effective diabetes management. Several factors should guide your decision, including pump features like touchscreen interfaces and remote monitoring, pump size and design for comfort, preferred insulin delivery method (tubing or tubeless), and considerations related to cost and insurance coverage for pump and supply expenses. Making an informed choice is crucial to suit your individual needs and lifestyle in diabetes care.
Insulin pumps have transformed diabetes management by offering greater precision, flexibility, and convenience. As a general physician, I encourage my patients to explore this option if it aligns with their needs and preferences. However, it’s essential to remember that successful diabetes management with an insulin pump requires education, regular monitoring, and ongoing communication with your healthcare team. By taking these steps, individuals with diabetes can lead healthier, more fulfilling lives while effectively managing their condition with the help of insulin pumps.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1) What are Advantages of insulin pumps?
Enhanced blood sugar control, reduced injections, precise dosing, meal timing flexibility, and potential for improved quality of life.
2) What are Disadvantages and risks?
Common disadvantages and risks of insulin pumps can include the cost of the device and ongoing supplies, the learning curve associated with pump use, the possibility of pump malfunctions, and the need for regular site changes and maintenance.
3) Can I disconnect the insulin pump for activities like swimming or showering?
Yes, you can disconnect the insulin pump for activities like swimming or showering, but consult your healthcare provider to manage your insulin during the disconnect.
4) How do I monitor my blood sugar levels while using an insulin pump?
Monitor blood sugar with fingerstick testing or Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) while using an insulin pump.
5) Can I travel with an insulin pump, and what precautions should I take?
Yes, you can travel with an insulin pump. To ensure a smooth journey, carry a letter from your healthcare provider explaining your medical need, pack extra supplies, and be prepared for security screenings at the airport.
References:
- A guide on Insulin pumps: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5922666/
- Insulin Pump: https://directorsblog.nih.gov/tag/insulin-pump/
- Diabetic Neuropathy: https://www.medtronicdiabetes.com/loop-blog/
- What Are Insulin Pumps? https://www.webmd.com/diabetes/insulin-pump
- Diabetes Technology Update https://diabetesjournals.org/care/Diabetes-Technology-Update-Use-of-Insulin-Pumps
About Author –
















 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More