Irritable Bowel Syndrome

At a Glance:
1. What is irritable bowel disease or irritable bowel syndrome?
2. What are the symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome?
3. What are the causes of irritable bowel syndrome?
4. What are the risk factors for irritable bowel syndrome?
5. How is irritable bowel syndrome diagnosed by doctors?
6. What are the treatment options for irritable bowel syndrome?
7. What is the recommended diet for irritable bowel syndrome?
8. What are the food items to avoid with irritable bowel syndrome?
9. What are the complications of irritable bowel syndrome?
What is irritable bowel disease or irritable bowel syndrome?
Affecting about 15% of the population, Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a common gastrointestinal disorder.
The exact cause of this condition remains unknown. Medications and lifestyle changes help to alleviate the symptoms of IBS. Unfortunately, IBS, in almost all the cases, remains lifelong and there is no permanent cure of the disease. Untreated and unmanaged, IBS significantly affects the quality of life.
IBS is also known as Brain-Gut disorder due to the involvement of the brain in the improper functioning of the gut. The sensitive gastrointestinal nervous system, family history of IBS, stress and fast movement of food through the gastrointestinal tract are some of the risk factors related to IBS.
The person with IBS may experience abdominal pain, fullness, chronic constipation, change in bowel habits and bloating.
Chronic constipation, in some people, may lead to haemorrhoids. Women are typically more affected with IBS as compared to men, and it is common in people with age less than 45 years. IBS does not increase the risk of gastrointestinal cancer.
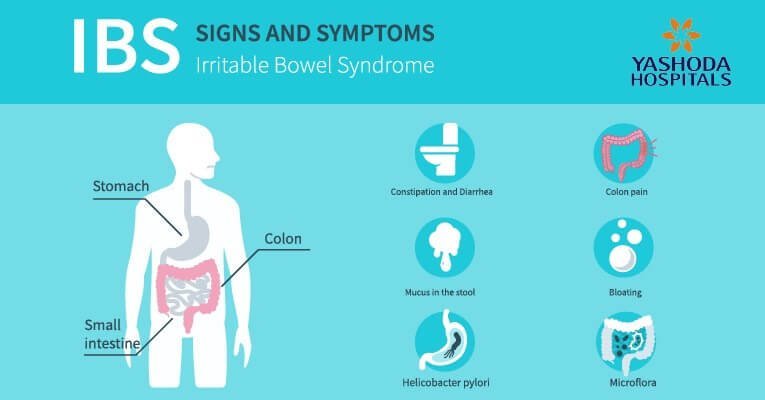
What are the symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome?
The symptoms of IBS may overlap with other serious conditions. If you have any symptom related to the gastrointestinal tract that may concern you, immediately consult with your doctor. Some of the common symptoms of IBS include:
Stomach Pain: Person with IBS experiences stomach pain and cramping which becomes severe after eating. The pain is eased by having a bowel motion.
Change in bowel habits: Person with IBS witnesses change in their bowel habits. The person may have diarrhoea, constipation or bowel habit of mixed pattern with both diarrhoea and constipation.
Bloating: In some persons, the only symptom of IBS is bloating i.e. fullness of the abdomen, which may feel distended from morning to evening at times. Food may be the trigger for bloating. Bloating is often reduced by lying down.
Mucus in stools: Although it is normal to pass some mucus in the stools, the amount of mucus is increased in persons suffering from IBS.
Nausea: Persons with IBS also experience nausea like many other gastrointestinal disorders and the exact cause of nausea should be diagnosed for a better treatment approach.
On the basis of dominance of diarrhoea and constipation, IBS is generally divided into three categories:
Diarrhea Predominant: In this type of IBS, the person experiences moderate to severe diarrhoea. There is an urgent need to go to the toilet which cannot be delayed. Diarrhoea may be triggered initially in the mornings and progressively every time after eating.
Constipation-Predominant: The person with IBS suffers from chronic constipation. Constipation may lead to abdominal cramping. Further, people with prolonged constipation have the risk of haemorrhoids.
Alternating constipation and diarrhoea: Such type of IBS involves the alternate occurrence of diarrhoea and constipation.
What are the causes of irritable bowel syndrome?
A definitive cause of IBS is not known as yet. It is assumed that an abnormality in some physiological processes leads to IBS. The person may have altered gastrointestinal motility and have had a disruption in the gut-brain axis. Some probable causes of Irritable Bowel Syndrome are:
Movement of food: Change in food movement through the gastrointestinal tract may be the reason for a variety of symptoms in IBS. The speed of food movement may either be too slow or too quick. The change in this movement leads to a change in the bowel function. Further, the fast and slow movement of food also affects the digestive process leading to bloating and gas formation.
Muscular dysfunction: Food moves in the gastrointestinal tract through peristaltic movement regulated by muscles present in the inner lining. Both poor and strong muscular function results in IBS. Strong muscular functions for prolonged period results in diarrhoea. Similarly, bloating with poor muscular contraction results in constipation or hard, dry stools.
Altered neural stimulation: Performance of the nervous connection between the gastrointestinal tract and the brain (gut-brain axis) is regulated by chemical substances such as serotonin and gastrin. Abnormalities in the nervous system cause a greater amount of discomfort even due to minor changes in the gastrointestinal tract such as the formation of gas or rapid food movement that may result in cramping and diarrhoea.
Severe infection: Another common symptom of IBS, severe diarrhoea, is also caused due to the infection in the gastrointestinal tract. The infection may be caused due to either bacteria or virus.
Disrupted gut microflora: Many cases of IBS are characterized by a reduced level of good bacteria in the intestine. This leads to the dominance of disease-causing bacteria and results in intestinal infection.
Intestinal inflammation: As compared to a normal and healthy person, the gastrointestinal tract of the person suffering from IBS has increased invasion of immune cells. This increased immune cell and increased inflammation results in pain and diarrhoea.
What are the risk factors for irritable bowel syndrome?
The exact cause of irritable bowel syndrome is not known; however, various risk factors increase the incidence of this condition. Some risk factors for irritable bowel syndrome are:
Food allergy: Food allergy worsens the symptoms of IBS. Also, allergy to a particular food may flare-up Irritable Bowel Syndrome. People may have worsened IBS symptoms when they take cabbage, citrus fruits, wheat, milk and carbonated drinks.
Hormones: Hormones are also believed to be a risk factor. This belief is based in the high incidence of IBS in women as compared to men and worsening of symptoms during the menstrual period.
Stress: Stress is not the causative factor for irritable bowel syndrome, but stress for prolonged periods negatively affects the quality of life by worsening the symptoms of IBS.
Gender: Females are twice at risk for developing irritable bowel syndrome as compared to males. Risk is further increased because of estrogen therapy.
Family History: Genes are believed to have their involvement in the development of IBS. People with a family history of IBS are at comparatively high risk.
Mental Disorders: Depression and anxiety worsen the symptoms of IBS. Abuse of any type such as physical, sexual or emotional increases the risk of IBS.
Age: IBS generally affects people below the age of 50.
How is irritable bowel syndrome diagnosed by doctors?
Irritable bowel syndrome is diagnosed by preparing a thorough medical and family history and establishing a clinical correlation between symptoms and definition of IBS under certain standards such as Rome and Manning criteria. Through exclusionary diagnosis, the presence of other conditions is ruled out as there are no lab or imaging tests that give conclusive results about the presence of IBS. Conditions that are ruled out include infections, enzyme deficiency, inflammatory bowel diseases, side effects of medications or certain food allergies.
The symptoms of IBS overlap with the symptoms of some other serious medical conditions such as anaemia, rectal bleeding, fever, weight loss, persistent diarrhoea, etc.
Some of the supportive laboratory and imaging tests recommended for IBS include:
- Stool test: To determine the presence of bacteria or any other parasite.
- Breath test: IBS may be caused due to bacterial overgrowth in the gastrointestinal tract. The breath test is used to detect the presence of any bacterial overgrowth.
- Lactose intolerance test: Lactose intolerance may lead to bloating and diarrhoea after taking dairy products. This is due to the deficiency of the lactase enzyme.
- Blood tests: Blood tests are conducted to rule out the presence of other diseases such as anaemia.
Imaging tests:
- Colonoscopy: A procedure to look into the colon by inserting a narrow tube fitted with a camera on the front end. A colonoscopy helps in viewing any abnormality in the colon.
- Flexible sigmoidoscopy: Lower part of the colon is known as sigmoid. The doctor will examine the sigmoid to look for any inflammation or blockage.
- X-Ray: Imaging techniques such as X-ray or CT scan are performed in cases where the doctor needs to know the cause of abdominal pain and cramps.
What are the treatment options for irritable bowel syndrome?
Irritable bowel syndrome is a chronic condition without any permanent and definitive cure. The treatment strategy is directed to alleviate the symptoms and improve the quality of life. Medications that can be prescribed for irritable bowel syndrome are:
Laxatives: Constipation is one of the symptoms of IBS. The doctor may prescribe laxatives such as magnesium hydroxide or polyethylene glycol to relieve constipation. Apart from laxatives, fibre supplements may also be prescribed.
Anti-diarrhea medications: Anti-diarrhea medications prevent diarrhea.
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors and Tricyclic antidepressants: Drugs can be prescribed in case the person feels depressed and suffers from constipation and pain.
Pain relievers: Drugs recommended to treat neuropathic pain.
What is the recommended diet for irritable bowel syndrome?
While choosing the diet, a person should take care of the following:
- Incorporate high-fibre food in the diet.
- Drink plenty of fluid.
- Follow a low FODMAP diet (fermentable oligo-, di-, and monosaccharides and polyols).
- Have a low-fat diet as the quantity of fibre is less in a high-fat diet.
What are the food items to avoid with irritable bowel syndrome?
Some food items are likely to trigger symptoms of IBS, hence they should be avoided. Following are the recommendations in this regard:
- Avoid foods that may cause allergic reactions and maintain a food diary to check what kind of foods triggered your symptoms
- Avoid foods that result in increased gas formation such as cabbage, broccoli, raw vegetables, and carbonated drinks.
- Avoid gluten-rich foods such as wheat, rye and barley.
- Avoid easily fermentable foods by the digestive system containing sugars like oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides and polyols. Some of the examples of food items with such sugars are cookies, cakes, soft drinks, candy, apples, pears, mangoes, etc
A customized diet plan by a qualified dietician under supervision of an expert gastroenterologist is highly recommended.
What are the complications of irritable bowel syndrome?
Symptoms of IBS generally affect the quality of life. IBS neither increases the risk of cancer nor does it lead to a serious gastrointestinal disorder. Some of the complications of Irritable Bowel Syndrome are:
Dehydration: Chronic diarrhoea results in dehydration. During dehydration, the body loses fluid as well as essential minerals. The doctor may recommend the intake of plenty of water and juice.
Faecal impaction: If the constipation is prolonged, the stools are too hard to push out from the body leading to faecal impaction.
Malnourishment: Diet restrictions in IBS may relieve the symptoms but may also cause a reduced supply of nutrients. This, in the long run, causes malnutrition.
Haemorrhoids: Chronic constipation may cause the blood vessels surrounding the anus to get inflamed. There may be pain and bleeding.
Poor quality of life: IBS negatively impacts the quality of life and leads to poor job performance. It may increase the incidences of social isolation.
Mood disorders: Unmanaged or poorly managed symptoms of IBS may cause mood disorder in the person. The person may suffer from anxiety and depression.
Is it possible to prevent irritable bowel syndrome?
Irritable bowel syndrome can be prevented by managing the triggers that cause this condition. Some of the preventive measures are:
Boosting the immune system: Infection and inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract cause irritable bowel syndrome. To prevent infection, the immune system should be maintained at an optimum level.
Maintain normal gut flora: Gut flora balance should be maintained by supplementing with probiotics if required.
Avoid triggers: Triggers such as allergic foods, depression and anger should be avoided to prevent Irritable Bowel Syndrome.
Managing stress: Stress can either develop Irritable Bowel Syndrome or worsen symptoms. Stress should be managed through meditation, yoga or through counselling sessions.
Conclusion:
Irritable Bowel Syndrome is a chronic condition related to the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms of IBS are stomach pain and cramps, bloating, constipation or diarrhoea, nausea and increased mucus in stools. The exact cause of IBS is not known but the condition is believed to be caused by severe infection, abnormal gut-brain axis and inflammatory conditions. There is no permanent cure for this condition, but the symptoms can be managed through medications and lifestyle changes.
References:
- International Foundation for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders, Signs, and Symptoms. Available at: https://www.aboutibs.org/signs-and-symptoms-main.html. Accessed on June 3, 2019
- Mayo Clinic, Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/irritable-bowel-syndrome/symptoms-causes/syc-20360016. Accessed on June 3, 2019
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Available at: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/irritable-bowel-syndrome. Accessed on June 3, 2019
- American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons, Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Available at: https://www.fascrs.org/patients/disease-condition/irritable-bowel-syndrome-0. Accessed on June 3, 2019.
- NHS, Symptoms Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Available at: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/irritable-bowel-syndrome-ibs/symptoms/. Accessed on June 3, 2019.














 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More

