Blood Clot in Brain: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
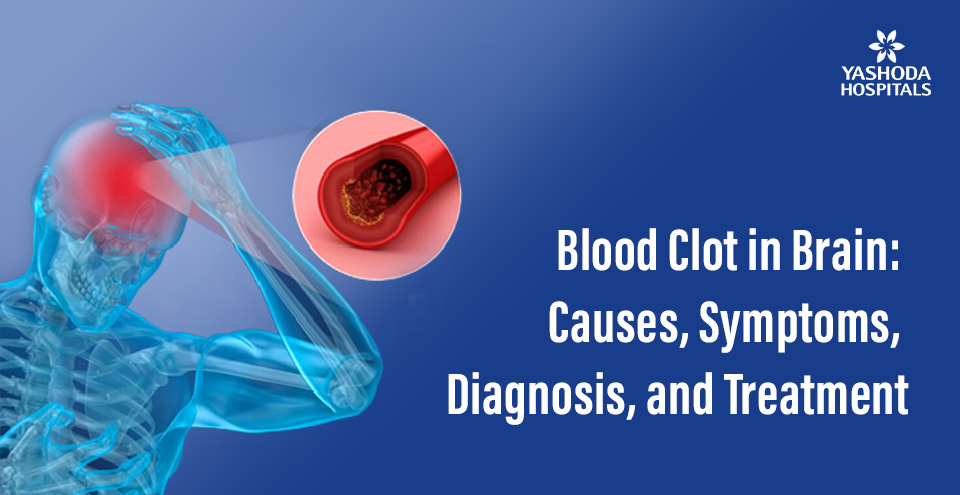
Blood clot in the brain is a terrifying and life-changing event that affects thousands of people every year. There are countless stories of individuals whose lives have been forever altered by a blood clot in the brain. The sudden onset of symptoms can be overwhelming and frightening, leaving individuals feeling helpless and scared. However, it is crucial to know that immediate medical attention can make all the difference in the outcome of a stroke. In this article, let’s explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for blood clots in the brain and highlight the importance of recognizing and responding to the warning signs of a stroke.
A blood clot in the brain, also known as cerebral thrombosis or a stroke, is a medical emergency that can lead to severe brain damage or even death. A blood clot forms when blood cells clump together and block a blood vessel in the brain. This blockage can prevent oxygen and nutrients from reaching the brain tissue, causing damage or death of the affected brain cells. In this article, let’s learn the types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for a blood clot in the brain.
Types of blood clots
There are two types of blood clots that can cause a stroke – ischemic and hemorrhagic.
- Ischemic Stroke: This type of stroke occurs when a blood clot forms in an artery that supplies blood to the brain. Ischemic strokes are the most common type of stroke, accounting for around 87% of all strokes.
- Hemorrhagic Stroke: A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures and leaks blood into the brain tissue. This type of stroke is less common but more severe and life-threatening than an ischemic stroke.
Did you know that the type of stroke one experiences could have a significant impact on their chances of survival in the long run?
Causes of blood clot in brain formation
The following are the most common causes or reasons for a blood clot in the brain:
- Atrial fibrillation: An irregular heartbeat can cause blood to pool in the heart which can lead to the formation of a blood clot that travels to the brain.
- High blood pressure: Hypertension damages the blood vessels and increases the risk of blood clots in the brain.
- Smoking: It can cause damage to the blood vessels and increase the risk of blood clot formation.
- Diabetes: Uncontrolled diabetes can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of blood clots.
- High cholesterol: Elevated levels of cholesterol in the blood can lead to the formation of blood clots.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of blood clots in the brain.
- Family history: If a family member has had a stroke or blood clot, your risk of developing one is higher.
- Age: As we age, the risk of blood clots in the brain increases.
Risk factors associated with a blood clot in the brain
While the blood clot in brain survival rate has improved over the years, it’s important to recognize the risk factors and take preventative measures. Several factors can increase a person’s risk of developing blood clots in the brain. Age, gender, smoking, high blood pressure, obesity, uncontrolled diabetes, high cholesterol, family history, and others are all risk factors for blood clots in the brain. One should be aware of these factors and take steps to reduce them through lifestyle changes and medical management.
Symptoms of a blood clot in the brain
The blood clot in the brain symptoms can vary depending on the location and size of the clot. Common symptoms include:
- Sudden weakness or numbness on one side of the body
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
- Loss of vision in one or both eyes
- Severe headache
- Dizziness or loss of balance
- Confusion or memory loss
- Seizures
- Nausea or vomiting
How to diagnose a blood clot in the brain?
To diagnose a blood clot in the brain, the doctor will perform some tests to determine the location, size, and severity of the clot. The following are the most common diagnostic tests for a blood clot in the brain:
- Physical exam: The doctor will assess the patient’s symptoms and check for signs of a stroke, such as weakness or numbness on one side of the body, difficulty speaking or understanding speech, sudden vision problems, severe headache, or dizziness.
- Imaging tests: A computed tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan can show if there is a blood clot or bleeding in the brain. These imaging tests create detailed images of the brain. Doppler ultrasound is a non-invasive test that uses sound waves to create images of the blood vessels in the neck and brain to check for blockages. This test can help in identifying any obstructions in the blood vessels that may be causing the blood clot.
- Blood tests: The doctor may perform blood tests to check for conditions that can increase the risk of blood clots, such as high cholesterol, high blood pressure, diabetes, or a genetic clotting disorder. These tests can help in identifying any underlying conditions that may be contributing to the formation of the blood clot.

How can you treat a blood clot in the brain?
The blood clot in the brain treatment is a complex and delicate process that requires immediate medical attention. The type and severity of the stroke will determine the best course of treatment. The following are the most common treatment options for a blood clot in the brain:
- Medications: Clot-busting drugs can be given to dissolve the clot and improve blood flow to the brain. These drugs are most effective when given within the first few hours of the stroke, and they carry a risk of bleeding complications. Anticoagulants or blood-thinning medications can also be given to prevent new blood clots from forming.
- Surgery: In severe cases, blood clot in brain surgery may be necessary to remove the blood clot or repair the damaged blood vessels in the brain. The most common surgical procedure for treating a blood clot in the brain is called a thrombectomy, which involves using a catheter to remove the clot from the blood vessel.
- Rehabilitation: After treatment, rehabilitation is necessary to help patients regain lost function and prevent future strokes. This may include physical therapy, speech therapy, occupational therapy, and other forms of therapy to help patients regain their strength, mobility, and cognitive function.
Prevention of blood clot in the brain
The following measures can help prevent a blood clot in the brain:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese increases the risk of blood clots.
- Exercise regularly: Regular exercise can improve blood flow and reduce the risk of blood clots.
- Quit smoking: Smoking damages the blood vessels and increases the risk of blood clots.
- Controlling underlying conditions: Blood clots are more likely to occur in individuals with underlying conditions like high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol. To prevent blood clots, it is essential to undergo regular health checkups to manage these conditions effectively.
- Eat a healthy diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can reduce the risk of blood clots.
- Drink alcohol in moderation: Drinking too much alcohol can increase the risk of blood clots.
A blood clot in the brain is a serious medical emergency that can lead to brain damage or even death. The key to preventing and treating a blood clot in the brain is to identify and manage the risk factors that contribute to its development. If you experience any of the symptoms of a stroke, seek medical attention immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve your chances of recovery and prevent further damage to your brain.
References:
- Blood Clots
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17675-blood-clots - Long-Term Survival Rate After a Stroke
https://www.verywellhealth.com/stroke-survival-rate-5213990












 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More

