Understanding Adrenalectomy: The Complete Guide to Adrenal Gland Removal

3. What are the Types of Adrenalectomy?
5. Adrenalectomy Complications
6. How Surgeons Minimize Risks of Adrenalectomy Surgery?
8. Dietary and Lifestyle Adjustments After Adrenalectomy
9. How to Monitor Hormone Levels After Adrenalectomy?
10. When to Seek Help from a Doctor?
11. Innovations in Adrenalectomy: The Role of Robotics and AI
Adrenalectomy is commonly referred to as the surgical process of removing any of the adrenal glands, which sit on the upper poles of the kidneys. These glands secrete hormones that influence a number of physiological activities, including blood pressure and metabolism, as well as responses to stress. This surgery has the effect of generally improving health standards and, in some cases, even preventing more serious complications from developing. Modern medicine pays greater attention to adrenalectomy as a surgical procedure that has been improved in approaches and outcomes in terms of minimal invasiveness and techniques used, and technologies have advanced in years. This blog delivers detailed information regarding the adrenalectomy.
What is an Adrenalectomy?
Adrenalectomy is the surgical removal of one or both adrenal glands, which are positioned on top of either kidneys that control development and growth, metabolism, and sexual function. If one gland is removed, the other will assume the work of both; hormone replacement medicine will be needed until the other gland begins to function properly. Total removal of the entire adrenal glands may require lifelong hormone replacement medication. The surgeons can perform a laparoscopic adrenalectomy in most of the cases, as it involves usually one to four small incisions, and in some cases opt for the open surgery based on the patient’s condition.
One may need to have an adrenalectomy if he/she has adrenal cancer in one or both glands or if the glands are producing excessive hormones.
Who Needs Adrenalectomy?
There are some common indications of adrenalectomy that make the person want to get their adrenal gland removed. Below are the clinical indications for adrenalectomy:
- Presence of a functional adrenal mass seen on imaging.
- Primary aldosteronism (a condition where the adrenal glands produce too much aldosterone).
- Adrenal Cushing’s syndrome (a condition caused by the body producing too much cortisol).
- Pheochromocytoma (rare abnormal tumor growth that leads to excess adrenaline production).
- Presence of an abdominal or retroperitoneal mass >4 cm in pre-plan imaging.
- Adrenocortical neoplasia (tumor growth on adrenal glands).
Worried About Adrenal Gland Problems? Don’t Wait.
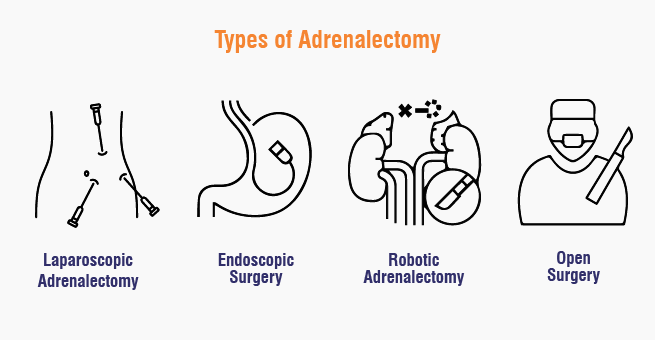
What are the Types of Adrenalectomy?
There are specific types of adrenalectomy procedures that are usually performed, such as:
- Unilateral adrenalectomy: This is performed to remove only one adrenal gland.
- Bilateral adrenalectomy: This is performed to remove both adrenal glands in cases of bilateral adrenal hyperplasia or tumors.
- Partial adrenalectomy: This is performed to remove the part of the adrenal gland.
Based on the type of approach, the adrenalectomy types are
- Laparoscopic adrenalectomy: This is minimally invasive and requires small incisions in the abdomen.
- Endoscopic surgery: This surgery is performed by a specialized endoscope and camera to access the adrenal gland.
- Robotic adrenalectomy: In this procedure, the surgeon employs robotic arms to meticulously dissect and remove the adrenal gland.
Open surgery: This is traditional and requires a larger incision for large tumors or complex cases.
Note: The type of surgery to be done mainly depends on the patient’s condition, type of tumor and location, and severity of the condition.
Adrenalectomy Procedure
- Laparoscopic adrenalectomy: A laparoscopic adrenalectomy is a procedure that is a step further from conventional surgery as it employs small cuts and instruments to get to the adrenal gland. This procedure requires making three to four small cuts in the abdomen, through which a laparoscope along with other tools are introduced to excise the affected adrenal gland. The gland is then placed in an endobag and removed without being ruptured. Laparoscopic adrenalectomy surgery is done with the patient undergoing general anesthesia, and it usually takes an hour to two hours. Patients report less pain after surgery, faster recovery times, shorter hospital stays, an earlier return to work, and more favorable cosmetic results compared to open surgery for noncancerous tumors.
- Robotic adrenalectomy: The robotic arms provide a magnified view of the adrenal gland and its surrounding tissues through a small incision in the abdomen. One of these incisions is utilized to place a high-definition camera under which the surgeon would have had the capability of dissecting and removing the adrenal gland with much care. The procedure is safe and efficient with the robotic arms controlled by a surgeon who is at a console. The incisions are closed with sutures or glue.
- Open adrenalectomy: Open adrenalectomy is a surgical technique that entails a wide abdominal incision to access the adrenal gland for its removal. This technique is often adopted in cases where the tumor is rather large, intricate, or situated in a region that is hard to access. In particular, open adrenalectomy, the surgeon cuts through the abdomen at the side, usually at the section that lies between the neck and hip. The surgeon attentively separates the tumor from the surrounding structure and extracts the tumor. After that, the stitches or staples can be applied.
The open method of adrenal gland removal is an extensive process that takes longer to recover as opposed to the other ways of doing it. This too is several times out of hospital and often has a period day or week range at best outlined.
Adrenalectomy Complication
Like with any surgical procedure, risks can arise. There is a higher probability of this occurring with an open adrenalectomy compared to a laparoscopic or robotic adrenalectomy. Possible complications of adrenalectomy include:
- Secondary infections.
- Excessive bleeding.
- Injury to adjacent structures.
- Development of hernias.
- Delayed healing of the surgical site.
- Effects of general anesthesia.
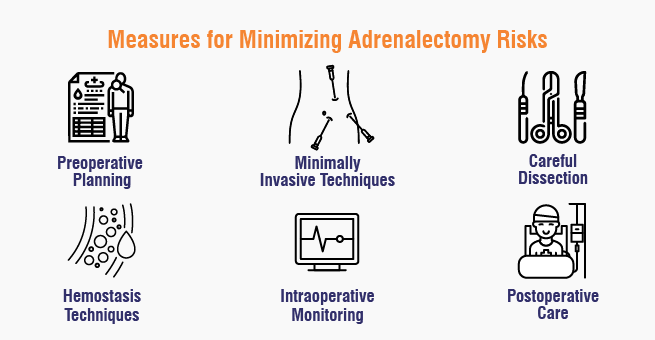
How Surgeons Minimize Risks of Adrenalectomy Surgery?
Adrenalectomy poses several risks, but surgeons are able to implement the following measures to control them:
- Preoperative planning: Adequate preoperative planning, such as diagnostic imaging, and input from other professionals help in pinpointing what the risks are and the best way to deal with surgical intervention.
- Minimally Invasive Techniques: Where applicable, laparoscopic or endoscopic adrenalectomy, which involves smaller incisions, is preferred, as this reduces the chances of complications and fastens recovery.
- Careful Dissection: Since adrenal glands are located adjacent to important body structures, surgeons pay close attention to dissection so as not to injure such structures.
- Hemostasis Techniques: These are techniques that are advanced and help in minimizing the amount of blood loss and the complications anticipated when carrying out surgeries.
- Intraoperative Monitoring: There is constant vigilance of parameters such as heart rate and blood pressure to detect and rectify any problems that may arise during the procedure.
- Postoperative Care: Upkeep of proper monitoring and control of pain, bleeding, or even infections after the surgical operation is very important for the healing process.
Not only the above measures, but the risk minimization will also depend on the surgeon’s skills and expertise as well as techniques used.
Adrenalectomy Recovery
The recovery time for adrenalectomy varies from patient to patient, type of surgery, overall health, and possible complications following surgery. Open adrenalectomy surgery requires a hospital stay of 5 to 7 days, while laparoscopic adrenalectomy recovery time can last between 2 and 3 days, requiring full recovery times within weeks to months. Patients in good general health have a faster recovery.
Dietary and Lifestyle Adjustments After Adrenalectomy
After an adrenalectomy procedure has been completed, it is necessary to adhere to a set of dietary and lifestyle recommendations, including:
- Salt intake should be monitored to avoid any interference with blood pressure.
- Potassium supplements should be taken for maintaining the level of electrolytes.
- Hydration should be maintained to keep blood pressure under control.
- Over-intake of caffeine and alcohol should be avoided to avoid fluctuations of hormones within the body.
- Stress needs to be controlled through practices such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Follow up check-ups with the doctor for tracing the hormone levels.
- Strenuous activities should not be performed before getting a green signal from the doctor.
- Adhere to prescribed medications and return any related side effects to the doctor or changes in symptoms.
How to Monitor Hormone Levels After Adrenalectomy?
Adrenalectomy, or surgical removal of the adrenal glands, interferes with the balance of hormones in the human body; therefore, regular follow-up is necessary for good health and to prevent complications. Blood tests could measure cortisol, aldosterone, and other hormones produced by the adrenal glands; urine tests are often taken; saliva tests measure cortisol at a specific point in time. Residual monitoring is necessary in order to obtain optimal health benefits and to prevent complications.
When to Seek Help from a Doctor?
If one experiences any of the following, it is important to see a doctor.
- Excessive weight gain or loss
- Fatigue or weakness
- High blood pressure
- Low blood pressure
- Rapid heartbeat
- Sweating
- Headaches
- Muscle weakness
- Increased urination
- Increased thirst
These can be symptoms of an underlying disorder affecting your adrenal glands, in the form of conditions such as Cushing’s syndrome or Conn’s syndrome, or a pheochromocytoma. The earlier that diagnosis and the following treatment occur, the easier it would be to prevent associated complications from worsening your health enough.
Innovations in Adrenalectomy: The Role of Robotics and AI
Robotics and AI enhanced the domain of adrenalectomy surgery, and it is now possible to proceed with minimally invasive as well as robotic surgeries in order to visualize intraoperative navigation and predictive analytics with a personalized postoperative treatment plan. It also minimizes the pain while abating scarring and shortening recovery time to thus result in a proper treatment end.
Yashoda Hospitals in Hyderabad, India, is incorporating innovative techniques in adrenalectomy, including minimally invasive techniques, advanced imaging, intraoperative monitoring, and specialized surgical teams to provide high-quality care and improved outcomes. It also ensures the patient’s safety and supports every person in terms of shorter recovery, prognosis, and overall well-being.
References:
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559093/
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/procedures/adrenalectomy-adrenal-gland-removal
- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/adrenalectomy
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/adrenalectomy/about/pac-20385243#:~:text=An%20adrenalectomy%20













 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More

